Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is a viral illness caused by the monkeypox virus.The virus was first identified in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is believed to have originated in African rainforests, with small mammals such as squirrels and monkeys acting as natural reservoirs. The virus can spread to humans through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids, and human-to-human transmission occurs through close contact, including skin-to-skin contact, respiratory droplets, and contaminated objects.
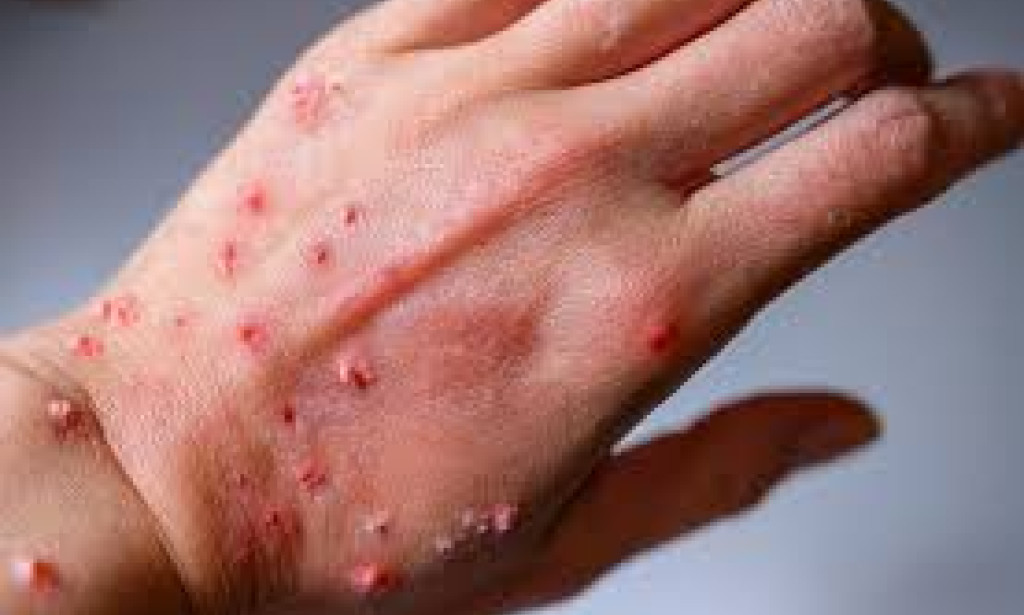
Mpox causes symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen lymph nodes, and a distinctive rash that progresses from macules to pustules and finally scabs. While most people recover without complications, the disease can be severe, especially in children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Prevention strategies include vaccination, avoiding close contact with infected individuals or animals, practicing good hygiene, and using personal protective equipment when caring for those infected.
In recent months, there has been a significant rise in mpox cases, particularly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and neighboring countries. The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) reported that the African region is still averaging about 2,800 new cases a week, with Uganda and Burundi experiencing sharp increases in infections. The spread of the virus has been driven by cross-border transmission and sexual contact, with new clusters emerging among sex workers. Efforts to control the outbreak include vaccination campaigns and enhanced surveillance measures.
It's good when people get educated about such diseases.
Knowledge is power
Great job writer😊
You must be logged in to post a comment.